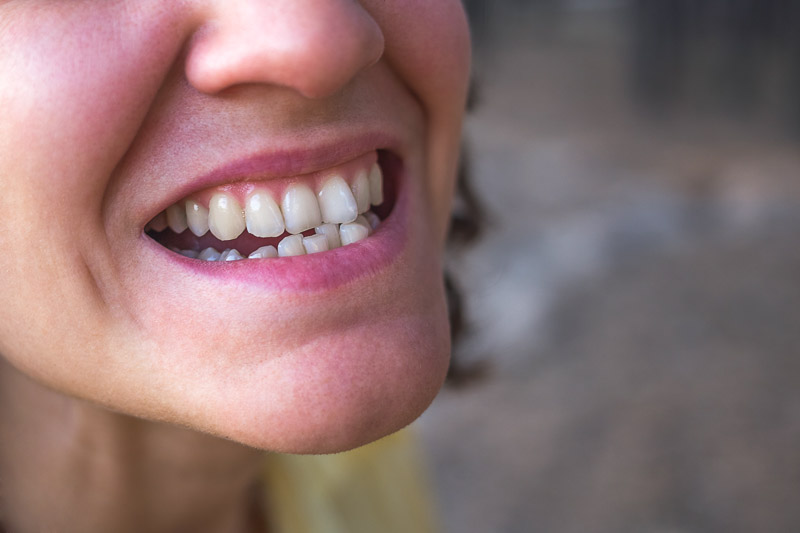

Types of crossbite?
There are two types of crossbite: anterior and posterior crossbites. Let's talk briefly about the two types.
1-Anterior crossbites occur in the front teeth and can cause the upper teeth to be behind the lower teeth. Anterior crossbites can cause a person's front teeth to appear "sunken".
2-Posterior crossbites occur in the back teeth and can cause the upper back teeth to be placed inside the lower back teeth. Posterior crossbites can give the impression that the back teeth are "collapsed."
Types of crossbite?
There are two types of crossbite: anterior and posterior crossbites. Let's talk briefly about the two types.
1. Anterior crossbites occur in the front teeth and can cause the upper teeth to be behind the lower teeth. Anterior crossbites can cause a person's front teeth to appear "sunken".
2.posterior crossbites occur in the back teeth and can cause the upper back teeth to be placed inside the lower back teeth. Posterior crossbites can give the impression that the back teeth are "collapsed."

Causes of cross-occlusion :
1. Dental or skeletal problems
A crossbite can be caused by dental problems such as misaligned teeth, crowded teeth or irregular eruption.
2. genetic factors
Genetics can contribute to the development of a crossbite. People born with a smaller upper jaw and a larger lower jaw may have narrower palates and dental anomalies, increasing their chances of developing a crossbite.
3. trauma and other factors
Habits such as mouth-breathing or thumb-sucking in children can cause crossbites. Other factors, such as accidents that can cause trauma, can also lead to crossbites.
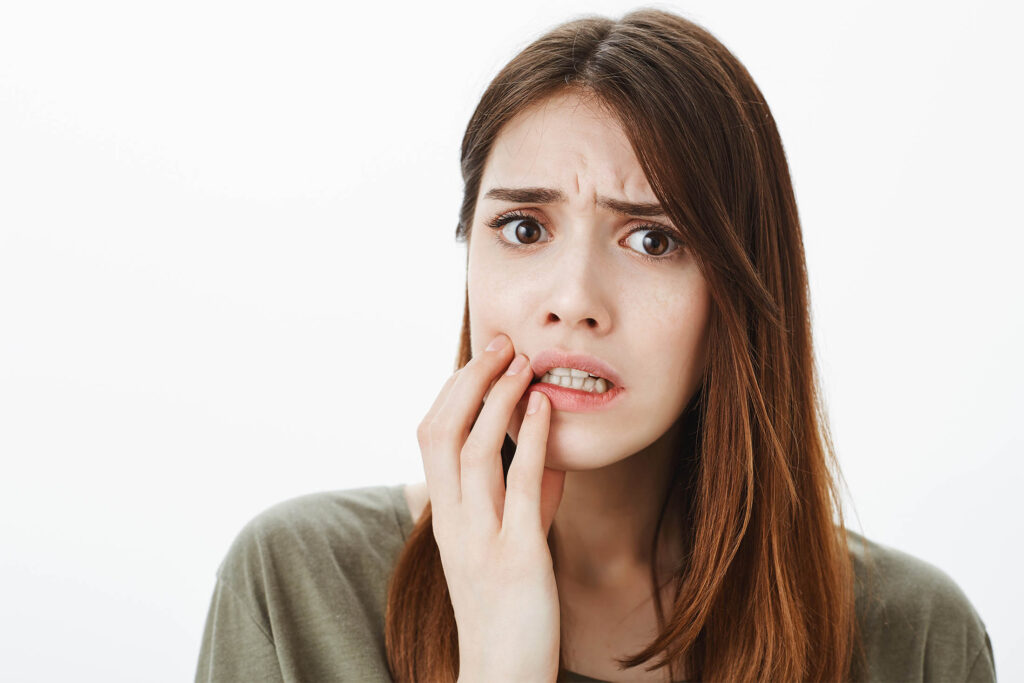

Symptoms of cross-occlusion:
1. Discomfort or pain during chewing
Misalignment of the jaw can cause discomfort or pain when biting and chewing food.
2. Language difficulties
Crossbite can affect the position of the teeth and jaw, causing difficulty in speaking or in pronouncing certain sounds.
3. Facial asymmetry
jaw misalignment can lead to facial asymmetry, with one side of the face appearing larger or more prominent than the other.
4. Jaw problems
Jaw problems such as TMJ, which can cause jaw pain, clicking or locking, are also symptoms of crossbite.
Symptoms of cross-occlusion:
1. Discomfort or pain during chewing
Misalignment of the jaw can cause discomfort or pain when biting and chewing food.
2. Language difficulties
Crossbite can affect the position of the teeth and jaw, causing difficulty in speaking or in pronouncing certain sounds.
3. Facial asymmetry
jaw misalignment can lead to facial asymmetry, with one side of the face appearing larger or more prominent than the other.
4. Jaw problems
Jaw problems such as TMJ, which can cause jaw pain, clicking or locking, are also symptoms of crossbite.

Why is it necessary to correct a crossbite?
Correcting a crossbite is important for several reasons. Firstly, a crossbite can cause discomfort, pain and difficulty chewing, which can affect a person's quality of life. It can also lead to speech difficulties and even jaw problems.
In addition to these immediate concerns, a crossbite can also cause long-term dental problems. For example, a crossbite can lead to tooth wear, gum recession and tooth decay. It can also lead to tooth loss or gum disease if left untreated.
What's more, in severe cases, a transverse bite can affect a person's appearance. It can cause facial asymmetry or alter the shape of a person's face, which can have a negative impact on self-esteem and confidence.
Overall, correcting a crossbite is important for immediate and long-term dental health, as well as general well-being and self-confidence. It's important to seek treatment as early as possible to avoid these complications and improve overall oral health.
